Joe works as an IT administrator in an organization and has recently set up a cloud computing service for the organization. To implement this service, he reached out to a telecom company for providing Internet connectivity and transport services between the organization and the cloud service provide. In the NIST cloud deployment reference architecture, under which category does the telecom company fall in the above scenario?
Option 1 : Cloud auditor
Option 2 : Cloud consumer
Option 3 : Cloud carrier
Option 4 : Cloud broker
1. Cloud auditor
A cloud auditor is a party that can perform an independent examination of cloud service controls with the intent to express an opinion on it. Audits are performed to verify conformance to standards through review of objective proof. A cloud auditor will evaluate the services provided by a cloud provider in terms of security controls, privacy impact, performance, etc.
Auditing is especially important for federal agencies as “agencies contractual embody a contractual clause enabling third parties to assess security controls of cloud providers”.
Cloud Security Audit?
Security controls are the management, operational, and technical safeguards or countermeasures employed within an organizational information system to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system and its info.
For security auditing, a cloud auditor will build an assessment of the security controls within the system to determine the extent to that the controls are implemented properly, operating as meant, and manufacturing the required outcome with reference to the security requirements for the system.
The security auditing should also include the verification of the compliance with regulation and security policy. as an example, an auditor will be tasked with ensuring that the right policies are applied to data retention in line with relevant rules for the jurisdiction. The auditor might ensure that fixed content has not been changed which the legal and business data archival requirements are glad.
A privacy impact audit will help Federal agencies comply with applicable privacy laws and laws governing an individual’s privacy, and to confirm confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an individual’s personal info at each stage of development and operation.
2. Cloud client
The cloud client is that the principal stakeholder for the cloud computing service. A cloud client represents someone or organization that maintains a account with, and uses the service from a cloud provider. A cloud client browses the service catalog from a cloud provider, requests the acceptable service, sets up service contracts with the cloud provider, and uses the service.
The cloud client is also beaked for the service provisioned, and needs to arrange payments accordingly. Cloud consumers fulfilled SLAs to specify the technical performance necessities fulfilled by a cloud provider. SLAs will cover terms regarding the quality of service, security, remedies for performance failures.
A cloud provider may also list within the SLAs a collection of promises explicitly not created to consumers, i.e. limitations, and obligations that cloud consumers should accept. A cloud client will freely select a cloud provider with better pricing and a lot of favourable terms.
Typically, a cloud provider’s evaluation policy and SLAs are non-negotiable, unless the customer expects serious usage and can be able to negotiate for better contracts.
Depending on the services requested, the activities and usage scenarios will be totally different among cloud consumers.
Below figure presents some example cloud services available to a cloud client (For details, see Appendix B: examples of Cloud Services).
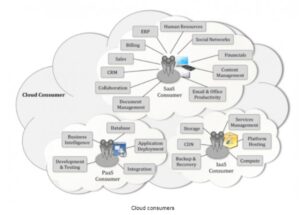
3. Cloud carrier
A cloud carrier acts as an intermediary that provides connectivity and transport of cloud services between cloud consumers and cloud providers.
Cloud carriers provide access to consumers through network, telecommunication and other access devices. for instance, cloud consumers will obtain cloud services through network access devices, like computers, laptops, mobile phones, mobile web devices (MIDs), etc.
The distribution of cloud services is often provided by network and telecommunication carriers or a transport agent, wherever a transport agent refers to a business organization that provides physical transport of storage media like high-capacity hard drives.
Note that a cloud provider can started SLAs with a cloud carrier to provide services consistent with the level of SLAs offered to cloud consumers, and will require the cloud carrier to provide dedicated and secure connections between cloud consumers and cloud providers.
4. Cloud broker
As cloud computing evolves, the integration of cloud services will be too advanced for cloud consumers to manage. A cloud consumer might request cloud services from a cloud broker, consumer contacting a cloud provider directly.
Who is Cloud Broker?
A cloud broker is an entity that manages the use, performance and delivery of cloud services and negotiates relationships between cloud providers and cloud consumers.
In general, a cloud broker can provide services in 3 categories:
Service Intermediation: A cloud broker enhances a given service by improving some specific capability and providing value-added services to cloud consumers. the improvement can be managing access to cloud services, identity management, performance enhanced, enhanced security, etc.
Service Aggregation: A cloud broker combines and integrates multiple services into one or more new services. The broker provides data integration and ensures the secure information movement between the cloud consumer and multiple cloud providers.
Service Arbitrage: Service arbitrage is like service aggregation except that the services being aggregated are not fixed. Service arbitrage suggests that a broker has the pliability to settle on services from multiple agencies. The cloud broker, for instance, will use a credit-scoring service to live and choose center with the most effective score.
Learn CEH & Think like hacker
- What is Ethical Hacking? & Types of Hacking
- 5 Phases of Hacking
- 8 Most Common Types of Hacker Motivations
- What are different types of attacks on a system
- Scope and Limitations of Ethical Hacking
- TEN Different Types Of Hackers
- What is the Foot-printing?
- Top 12 steps for Footprinting Penetration Testing
- Different types of tools with Email Footprinting
- What is “Anonymizer” & Types of Anonymizers
- Top DNS Interrogation Tools
- What is SNMP Enumeration?
- Top vulnerability scanning tools
- Information Security of Threat
- Footprinting tools:
- What is Enumeration?
- Network Security Controls
- What is Identity and Access Management?
- OWASP high TEN web application security risks
- Password Attacks
- Defend Against Key loggers
- Defend Against Spyware
- Covering Tracks
- Covering Track on Networks
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 1
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 2
- Learn more about GPS Spyware & Apparatuses
- Introduction of USB Spyware and It’s types
- 10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About
- Concepts of Denial-of-Service Attack & Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- Most Effective Ways to Overcome Impersonation on the Social Networking Site’s Problem
- How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works
- DHCP Request/Reply Messages
- DHCP Starvation Attack
- Rogue DHCP Server Attack
- IOS Switch Commands
- Web Server Concept
- Web Server Attacks
- Web Server Attack Tools
- Web Server Security Tools
- 6 Quick Methodology For Web Server Attack
- Learn Skills From Web Server Foot Printing / Banner Grabbing
- The 10 Secrets You Will Never Know About Cyber Security And Its Important?
- Ways To Learn Finding Default Content Of Web Server Effectively
- How will Social Engineering be in the Future
- Understand The Background Of Top 9 Challenges IT Leaders Will Face In 2020 Now
- Learning Good Ways To Protect Yourself From Identity Theft
- Anti-phishing Tools Guide
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



