Here’s a quick primer to distinguish related concepts to bring the Internet, Intranets, and Extranets this topics together:
- Internet: This is the global interconnection of networks public and It combines and connects the TCP/IP transport of data across WANs. The Internet was designed and launched by the U.S. Department of Defense but today is managed and operated by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
- Intranet: This is a type of network that is a diverse range of telecommunications services limited logically to internal The intranet runs on a corporate or privately controlled network infrastructure. The principle difference between an intranet and the Internet is that the former is bound by a controlled perimeter. That perimeter might be within a corporate building or might include some off-site or cloud portions. Intranets host organizational websites that are not externally accessible via the World Wide Web.
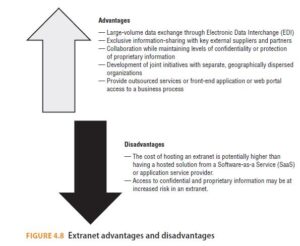
- Extranet: An extranet is a controlled private network that allows access to partners, vendors, and suppliers or an authorized set of customers. The access and information available are typically less controlled than the intranet, but more constrained than a publicly facing website. An extranet is similar to a DMZ because it allows the required level of access without exposing the entire organization’s network.
See Figure 4.8 for a comparative list of advantages and disadvantages of hosting an extranet.