OSI Layer 5: Session Layer
Module Objectives
- List the concepts and architecture that define the associated technology and implementation systems and protocols at Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers 1–7. (Session Layer)
- Define related threats and select appropriate countermeasures for systems and protocols operating at Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers 1–7. (Session Layer)
Concepts and Architecture
The session layer provides a logical persistent connection between peer hosts. The session layer is responsible for creating, maintaining, and tearing down the session.
Technology and Implementation
Session layer protocols include the following:
- PAP – password authentication protocol
- PPTP – Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
- RPC – remote procedure call protocol
RPCs represent the ability to allow for the executing of objects across hosts with a client sending a set of instructions to an application residing on a different host on the network. It is important to note that RPC does not in fact provide any services on its own; instead, it provides a brokering service by providing (basic) authentication and a way to address the actual service.
Threats and Countermeasures
ISO 7498 -2 specifies that no security services are provided in the session layer; therefore, it is imperative to address vulnerabilities revealed in the session layer by applying security services either above or below the session layer. A common methodology is to secure risky protocols that are still needed by means of encryption.
OSI Layer 6: Presentation Layer
Module Objectives
- List the concepts and architecture that define the associated technology and implementation systems and protocols at Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers 1–7. (Presentation Layer)
- Define related threats and select appropriate countermeasures for systems and protocols operating at Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers 1–7. (Presentation Layer)
Concepts and Architecture
The presentation layer maintains that communications delivered between sending and receiving computer systems are in a common and discernable system format.
Technology and Implementation
Translation Services
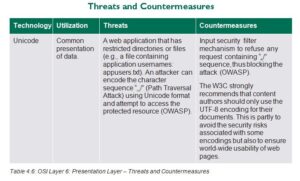
To provide a reliable syntax, systems processing at the presentation layer will use American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) or Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC) to translate from Unicode. In 2016 the W3C Internationalization Working Group estimated that 86 percent of all web pages sampled showed that they are using UTF 8 Unicode character encoding. It further states, “Not only are people using UTF-8 for their pages, but Unicode encodings are the basis of the Web itself. All browsers use Unicode internally, and convert all other encodings to Unicode for processing. As do all search engines. All modern operating systems also use Unicode internally. It has become part of the fabric of the Web.”
Translation services are also necessary when considering that different computer platforms (Macintosh and Windows personal computers) may exist within the same network and could be sharing data. The presentation layer is needed to translate the output from unlike systems to similar formats.
Conversion and Compression Services
Data conversion or bit order reversal and compression are other functions of the presentation layer. As an example, an MPEG-1 Audio Layer-3 (MP3) is a standard audio encoding and compression algorithm that creates a file with a bitrate of 128kbit/s. The Waveform Audio File Format (WAVE) with Linear PCM bitstream is another standard audio encoding and compression that creates a file with a bitrate of 44.1khz. The compression for both formats is accomplished at the presentation layer. If a tool is used to convert one format into another, this is also accomplished at the presentation layer.
Encoding
Encryption services such as TLS/SSL are managed below, above, and within the presentation layer. At times, the encoding capabilities that are resident at the presentation layer are inappropriately conflated with a specific set of cryptographic services. Abstract Syntax Notation (ASN.1) is an ISO standard that addresses the issue of representing, encoding, transmitting, and decoding data structures. The transfer of data entities between two points of communication could appear as nonsensical or encoding if a nonparticipating (eavesdropping) third party wasn’t aware of the standard being used in transmission.
Follow Us
https://www.facebook.com/INF0SAVVY
https://www.linkedin.com/company/14639279/admin/


