Sam is working as a system administrator in an organization . He captured the principle characteristics of a vulnerability and produced a numerical score to reflect its severity using CVSS v3.0 to properly assess and prioritize the organization’s vulnerability management processes. The base score that Sam obtained after performing CVSS rating was 4.0 What is CVSS severity level of the vulnerability discovered by Sam in the above scenario?
Option 1 : Critical
Option 2 : High
Option 3 : Medium
Option 4 : Low
1. Critical
Software, hardware and firmware vulnerabilities pose a critical risk to any organization operating a network , and may be difficult to categorize and mitigate. The Common Vulnerability rating system (CVSS) provides how to capture the principal characteristics of a vulnerability, and produce a numerical score reflecting its severity, also as a textual representation of that score. The numerical score can then be translated into a qualitative representation (such as low, medium, high, and critical) to assist organizations properly assess and prioritize their vulnerability management processes.
2. High
The full effect on the environmental score is decided by the corresponding Modified Base Impact metrics. That is, these metrics modify the environmental score by reweighting the Modified Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability impact metrics. for instance , the Modified Confidentiality impact (MC) metric has increased weight if the Confidentiality Requirement (CR) is High. Likewise, the Modified Confidentiality impact metric has decreased weight if the Confidentiality Requirement is Low. The Modified Confidentiality impact metric weighting is neutral if the Confidentiality Requirement is Medium. This same process is applied to the Integrity and Availability requirements.
Note that the Confidentiality Requirement won’t affect the Environmental score if the (Modified Base) confidentiality impact is about to None. Also, increasing the Confidentiality Requirement from Medium to High won’t change the Environmental score when the (Modified Base) impact metrics are set to High. this is often because the modified impact sub score (part of the Modified Base score that calculates impact) is already at a maximum value of 10.
3. Medium
For some purposes it’s useful to possess a textual representation of the numeric Base, Temporal and Environmental scores. All scores are often mapped to the qualitative ratings defined .
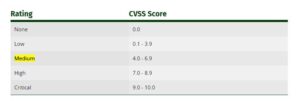
As an example, a CVSS Base score of 4.0 has an associated severity rating of Medium. the utilization of those qualitative severity ratings is optional, and there’s no requirement to incorporate them when publishing CVSS scores. they’re intended to assist organizations properly assess and prioritize their vulnerability management processes.
4. Low
The attacker is permitted with (i.e. requires) privileges that provide basic user capabilities that would normally affect only settings and files owned by a user. Alternatively, an attacker with Low privileges may have the power to cause an impression only to non-sensitive resources.
There is some loss of confidentiality. Access to some restricted information is obtained, but the attacker doesn’t have control over what information is obtained, or the quantity or quite loss is constrained. the knowledge disclosure doesn’t cause an immediate , serious loss to the impacted component.
Learn CEH & Think like hacker
- What is Ethical Hacking? & Types of Hacking
- 5 Phases of Hacking
- 8 Most Common Types of Hacker Motivations
- What are different types of attacks on a system
- Scope and Limitations of Ethical Hacking
- TEN Different Types Of Hackers
- What is the Foot-printing?
- Top 12 steps for Footprinting Penetration Testing
- Different types of tools with Email Footprinting
- What is “Anonymizer” & Types of Anonymizers
- Top DNS Interrogation Tools
- What is SNMP Enumeration?
- Top vulnerability scanning tools
- Information Security of Threat
- Footprinting tools:
- What is Enumeration?
- Network Security Controls
- What is Identity and Access Management?
- OWASP high TEN web application security risks
- Password Attacks
- Defend Against Key loggers
- Defend Against Spyware
- Covering Tracks
- Covering Track on Networks
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 1
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 2
- Learn more about GPS Spyware & Apparatuses
- Introduction of USB Spyware and It’s types
- 10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About
- Concepts of Denial-of-Service Attack & Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- Most Effective Ways to Overcome Impersonation on the Social Networking Site’s Problem
- How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works
- DHCP Request/Reply Messages
- DHCP Starvation Attack
- Rogue DHCP Server Attack
- IOS Switch Commands
- Web-Server Concept
- Web-Server Attacks
- Web-Server Attack Tools
- Web-Server Security Tools
- 6 Quick Methodology For Web Server Attack
- Learn Skills From Web Server Foot Printing / Banner Grabbing
- The 10 Secrets You Will Never Know About Cyber Security And Its Important?
- Ways To Learn Finding Default Content Of Web Server Effectively
- How will Social Engineering be in the Future
- Understand The Background Of Top 9 Challenges IT Leaders Will Face In 2020 Now
- Learning Good Ways To Protect Yourself From Identity Theft
- Anti-phishing Tools Guide
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



