Bill is a network administrator. He wants to eliminate unencrypted traffic inside his company’s network. He decides to setup a SPAN port and capture all traffic to the datacenter. He immediately discovers unencrypted traffic in port UDP 161. What protocol is this port using and how can he secure that traffic?
Option 1 : RPC and the best practice is to disable RPC completely
Option 2 : SNMP and he should change it to SNMP V2, which is encrypted
Option 3 : It is not necessary to perform any actions, as SNMP is not carrying important information
Option 4 : SNMP and he should change it to SNMP V3
1. RPC and the best practice is to disable RPC completely
The customary component for getting to an Exchange letter drop has consistently been to utilize a MAPI customer, for example, Outlook inside a corporate organization where distant method calls (RPCs) are utilized over TCP/IP. Trade 2003 presents the idea of a far off Outlook customer associating from any organization across firewalls utilizing RPC over HTTP associations. This new type of access acquaints new chances for associations with fall flat. In this segment, I’ll depict some helpful hints and procedures that you can use to investigate association issues, explicitly from Outlook RPC over HTTP protocol associations.
Configuring RPC over HTTP Connections
RPC over HTTP availability offers the absolute most noteworthy adaptability for customer associations with Exchange 2003. Utilizing the RPC Protocol over HTTP Protocol availability, Outlook 2003 can associate from basically any organization gave HTTP outbound access is accessible from the organization on which the Outlook customer is arranged. Be that as it may, RPC protocol over HTTP protocol availability has various requirements, and these are regularly the primary port of call with regards to investigating associations.
On the customer PC, you should be running Outlook 2003 and Windows XP SP1 with the fitting patch from Microsoft Product Support Service (PSS) (Quick Fix Engineering patch QFE331320). The forthcoming arrival of Windows XP SP2 will incorporate the essential fix. To be certain that you have the privilege working framework fix variant, you can check the rendition of the RPCRT4.DLL record situated in the <Windows directory>\ system32 catalog, where <Windows directory> addresses the drive and envelope wherein you’ve introduced Windows XP on the customer PC. Utilizing Windows Explorer, select the document, right-click, pick “Properties,” at that point the Version tab, at that point the “Record Version” thing: The base upheld rendition of the record is 5.1.2600.1142. The subtleties from my framework are appeared. This 5.1.2600.1142 form and later forms of the RPCRT4.DLL document settle an issue with Outlook customer defers while getting to the Exchange worker, explicitly utilizing RPC over HTTP.
Associating with the Exchange worker requires cautious design of your customer MAPI profile. You should guarantee that the MAPI profile is designed to permit RPC over HTTP port associations and that you indicate the RPC intermediary worker that will viably advance HTTP parcels from Outlook to the necessary Exchange back-end and worldwide list workers,
Microsoft has two executions of RPC over HTTP: forms 1 and 2. The RPC over HTTP usefulness actualized with Outlook 2003 utilizations adaptation 2. This is significant, in light of the fact that the two variants have various capacities. Variant 2 necessitates that Secure Socket Layer (SSL) correspondence be utilized and that the RPC intermediary worker confirm the association. This implies that the customer setup should indicate a SSL association and essential validation: Connections endeavored over non-SSL associations won’t work.
There are explicit variant prerequisites on the worker side too. The RPC intermediary worker should be running Windows 2003, as must any space regulators or worldwide inventory workers that the RPC intermediary worker will use to validate the customer association. What’s more, any worldwide index workers to which the client will be alluded ought to likewise be running Windows 2003. The Exchange back-end worker to which the client is eventually associated or some other Exchange workers (e.g., public organizer workers) should likewise be running Windows 2003 and Exchange 2003. Along these lines, the least complex dependable guideline here is to ensure that you have overhauled your whole framework to Windows 2003 workers and Exchange 2003 workers on Windows 2003 preceding you even consider executing RPC over HTTP access.
Controlling Connection Type Failover
At the point when you’ve empowered RPC over HTTP access, you’ll need to arrange the “On quick organizations, interface utilizing HTTP first, at that point associate utilizing TCP/IP” and the “On moderate organizations, interface utilizing HTTP first, at that point associate utilizing TCP/IP” settings. (Slow associations are those that are set up by Windows XP with a connection speed answered to Outlook 2003 of 115 Kbps or less.) Checking these crates guarantees that RPC over HTTP port associations are attempted first; on the off chance that an association can’t be made, at that point the convention flops over to TCP/IP. While this conduct is attractive during typical use, it is unwanted when initially endeavoring to arrange RPC protocol over HTTP protocol access for the straightforward explanation that Outlook will attempt to associate over HTTP, and, in the event that it comes up short, it will naturally interface utilizing conventional RPC protocol over TCP/IP protocol associations. This fizzle over is totally straightforward to the client, and you won’t realize that your RPC over HTTP association has truth be told fizzled and that you are associated through TCP/IP.
You can smother this programmed fall flat over element by setting the accompanying vault key:
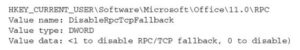
The objective of Outlook RPC over HTTP network is to make associations with Exchange as consistent as conceivable to the end client. That is, the Outlook client ought to identify no contrast between a customary RPC over HTTP association and a RPC over HTTP association. While incredible practically speaking, it is problematic during starting setup, since you can’t be sure about the convention being utilized to interface Outlook to Exchange except if you’ve incapacitated RPC over TCP/IP come up short finished, as depicted already. All in all, how might you decide how you are associated with your Exchange worker from Outlook? Indeed, you can utilize a basic stunt on the customer: With Outlook 2003 previously running, hold down the control key and simultaneously right-click on the Outlook symbol in the framework plate and select “Association Status.” This will yield an association status window that will recognize the current association type being used
2. SNMP and he should change it to SNMP V2, which is encrypted
Regardless of whether it be SNMP protocol traps or local area strings, there is a generally excellent possibility you have known about this veteran organization observing convention eventually in your vocation. With well more than twenty years of presence, the basic organization checking convention has given us simply that, essential knowledge into the strength of organization gadgets, workers and programming.
Basically, SNMP is a checking convention which works by inquiry. An organization checking device, for example, Ipswitch’s WhatsUp Gold or some other SNMP screen, will question a gadget or programming utilizing a SNMP OID (Object Identifier) or inquiry string.
The reaction back could be any worth identified with OID the questioned. For instance, it may restore a number 3 which for a Dell iDrac stockpiling exhibit signifies “Alright”. The questioning programming will realize which returned values address great wellbeing and those that don’t, giving a sign of wellbeing.
Notwithstanding this questioning or understanding activity, SNMP uphold compose capacities. As such, SNMP can be utilized to make arrangement changes on gadgets. Take for instance a Cisco Layer 3 switch, SNMP compose orders can be utilized to change the running arrangement record.
What is a SNMP Trap?
While SNMP is a questioning convention, it additionally incorporates the capacity to send cautioning messages when certain conditions emerge, for the most part crisis warnings like a bombed equipment segment. These messages are generally gotten by a similar organization checking apparatus or SNMP device to add to the general sign of gadget or application wellbeing.
This has to a great extent been supplanted by logging conventions, for example, Syslog, which give a lot more extravagant detail.
What is the Difference Between SNMP v1, v2C and v3?
SNMPv1 is the most seasoned and unique adaptation of the SNMP convention, supporting 32-cycle counters. SNMP v1 greatest imperfection is its utilization of a reasonable book local area string, which is utilized to recognize the gadget and structures a crude style of confirmation. With most gadgets utilizing the default local area string as “public” there is a huge danger of sneaking around or unapproved changes relying upon whether consents have been set to peruse just or compose.
SNMPv2c was made to ease the issue of the 32-digit counters, overhauling the conventions capacities to help 64-bit. The dangers encompassing the local area string actually remains.
SNMPv3 was perceived by the IETF in 2004. It adds a both encryption and verification alternatives to both forestall sneaking around and unapproved access. Set us is definitely more confounded than making a local area string yet mitigates large numbers of the dangers characteristic in SNMP v1 and v2c.
3. It is not necessary to perform any actions, as SNMP is not carrying important information
SNMP is definitely an exceptionally valuable convention for the administration and observing of organization gadgets, workers and applications. If it is secure truly boils down to the degree of danger which is adequate to the association.
SNMPv1 and v2c do have defects in that confirmation is practically non-existent. In any case, in the event that you do demand utilizing these conventions, it is suggested that you change the default local area and you confine SNMP to peruse as it were. Where it is conceivable, consistently attempt to utilize SNMPv3. Some heritage gadgets, workers and applications may need to moved up to help the more current convention. A potential operational issue however an absolute necessity for the best decrease of danger and the most noteworthy potential degrees of security.
It isn’t important to play out any activities, as SNMP isn’t conveying significant data
In run of the mill employments of SNMP, at least one authoritative PCs called administrators have the undertaking of observing or dealing with a gathering of hosts or gadgets on a PC organization. Each oversaw framework executes a product segment called a specialist which reports data by means of SNMP to the director.
A SNMP-oversaw network comprises of three key parts:
- Managed gadgets
- Agent – programming which runs on oversaw gadgets
- Network the board station (NMS) – programming which runs on the chief
An oversaw gadget is an organization hub that executes a SNMP interface that permits unidirectional (read-just) or bidirectional (peruse and compose) admittance to hub explicit data. Overseen gadgets trade hub explicit data with the NMSs. Once in a while called network components, the oversaw gadgets can be any sort of gadget, including, yet not restricted to, switches, access workers, switches, link modems, spans, centers, IP phones, IP camcorders, PC hosts, and printers.
A specialist is an organization the executives programming module that dwells on an oversaw gadget. A specialist has neighborhood information on administration data and makes an interpretation of that data to or from a SNMP-explicit structure.
An organization the executives station executes applications that screen and control oversaw gadgets. NMSs give the main part of the preparing and memory assets needed for network the board. At least one NMSs may exist on any oversaw network.
4. SNMP and he should change it to SNMP V3
We have various articles already in our documentation for setting up SNMPv2 trap handling in Opsview, but SNMPv3 traps are a whole new ballgame. They can be quite confusing and complicated to set up the first time you go through the process, but when you understand what is going on, everything should make more sense.
SNMP has gone through several revisions to improve performance and security (version 1, 2c and 3). By default, it is a UDP port based protocol where communication is based on a ‘fire and forget’ methodology in which network packets are sent to another device, but there is no check for receipt of that packet (versus TCP port when a network packet must be acknowledged by the other end of the communication link).
There are two modes of operation with SNMP – get requests (or polling) where one device requests information from an SNMP enabled device on a regular basis (normally using UDP port 161), and traps where the SNMP enabled device sends a message to another device when an event occurs (normally using UDP port 162). The latter includes instances such as someone logging on, the device powering up or down, or a wide variety of other problems that would need this type of investigation.
This blog covers SNMPv3 traps, as polling and version 2c traps are covered elsewhere in our documentation.
SNMP traps
Since SNMP is primarily a UDP port based system, traps may be ‘lost’ when sending between devices; the sending device does not wait to see if the receiver got the trap. This means if the configuration on the sending device is wrong (using the wrong receiver IP address or port) or the receiver isn’t listening for traps or rejecting them out of hand due to misconfiguration, the sender will never know.
The SNMP v2c specification introduced the idea of splitting traps into two types; the original ‘hope it gets there’ trap and the newer ‘INFORM’ traps. Upon receipt of an INFORM, the receiver must send an acknowledgement back. If the sender doesn’t get the acknowledgement back, then it knows there is an existing problem and can log it for sysadmins to find when they interrogate the device.
Learn CEH & Think like hacker
- What is Ethical Hacking? & Types of Hacking
- 5 Phases of Hacking
- 8 Most Common Types of Hacker Motivations
- What are different types of attacks on a system
- Scope and Limitations of Ethical Hacking
- TEN Different Types Of Hackers
- What is the Foot-printing?
- Top 12 steps for Footprinting Penetration Testing
- Different types of tools with Email Footprinting
- What is “Anonymizer” & Types of Anonymizers
- Top DNS Interrogation Tools
- What is SNMP Enumeration?
- Top vulnerability scanning tools
- Information Security of Threat
- Footprinting tools:
- What is Enumeration?
- Network Security Controls
- What is Identity and Access Management?
- OWASP high TEN web application security risks
- Password Attacks
- Defend Against Key loggers
- Defend Against Spyware
- Covering Tracks
- Covering Track on Networks
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 1
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 2
- Learn more about GPS Spyware & Apparatuses
- Introduction of USB Spyware and It’s types
- 10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About
- Concepts of Denial-of-Service Attack & Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- Most Effective Ways to Overcome Impersonation on the Social Networking Site’s Problem
- How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works
- DHCP Request/Reply Messages
- DHCP Starvation Attack
- Rogue DHCP Server Attack
- IOS Switch Commands
- Web Server Concept
- Web Server Attacks
- Web Server Attack Tools
- Web Server Security Tools
- 6 Quick Methodology For Web Server Attack
- Learn Skills From Web Server Foot Printing / Banner Grabbing
- The 10 Secrets You Will Never Know About Cyber Security And Its Important?
- Ways To Learn Finding Default Content Of Web Server Effectively
- How will Social Engineering be in the Future
- Understand The Background Of Top 9 Challenges IT Leaders Will Face In 2020 Now
- Learning Good Ways To Protect Yourself From Identity Theft
- Anti-phishing Tools Guide
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



