In order to tailor your during a web-application scan, you decide to determine which web-server version is hosting the application. On using the sV flag with Nmap, you obtain the following response: 80/tcp open http-proxy Apache Server 7.1.6 What information-gathering technique does this best describe?
Option 1 : Banner grabbing
Option 2 : Brute forcing
Option 3 : WHOIS lookup
Option 4 : Dictionary attack
1. Banner grabbing
Banner grabbing is a technique wont to gain info about a computer system on a network and the services running on its open ports. administrators will use this to take inventory of the systems and services on their network. However, an to find will use banner grabbing so as to search out network hosts that are running versions of applications and operating systems with known exploits.
Some samples of service ports used for banner grabbing are those used by Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP); ports 80, 21, and 25 severally. Tools normally used to perform banner grabbing are Telnet, nmap and Netcat.
For example, one may establish a connection to a target internet server using Netcat, then send an HTTP request. The response can usually contain info about the service running on the host:
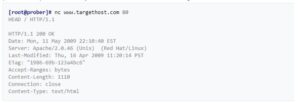
This information may be used by an administrator to catalog this system, or by an intruder to narrow down a list of applicable exploits.
To prevent this, network administrators should restrict access to services on their networks and shut down unused or unnecessary services running on network hosts. Shodan is a search engine for banners grabbed from portscanning the Internet.
2. Brute forcing
A brute force attack may be a common cracking method: by some accounts, brute force attacks accounted for 5 p.c of confirmed security breaches. A brute force attack involves ‘guessing’ username and passwords to achieve unauthorized access to a system. Brute force can be a may be a attack methodology and features a high success rate.
Some attackers use applications and scripts as brute force tools. These tools try numerous word combinations to bypass authentication processes. In alternative cases, attackers attempt to access internet applications by searching for the right session ID. attacker motivation may include stealing knowledge, infecting sites with malware, or disrupting service.
While some attackers still perform brute force attacks manually, these days almost all brute force attacks these days ar performed by bots. Attackers have lists of normally used credentials, or real user credentials, obtained via security breaches or the dark web. Bots systematically attack websites and take a look at these lists of credentials, and notify the attacker once they gain access.
3. WHOIS lookup
The information about the users that own registered domains is contained within the Whois info. the data regarding the owner of the website can be retrieved using the Whois info. the personal info about the owners of the site like server’s informatics address, physical address, email address, phone number, registration date of website, expiry date of website, etc.
4. Dictionary attack
A dictionary attack may be a method of breaking into a word-protected computer or server by consistently coming into each word during a dictionary as a password. A dictionary attack can also be used in a shot to hunt out the key necessary to decrypt an encrypted message or document.
Learn CEH & Think like hacker
- What is Ethical Hacking? & Types of Hacking
- 5 Phases of Hacking
- 8 Most Common Types of Hacker Motivations
- What are different types of attacks on a system
- Scope and Limitations of Ethical Hacking
- TEN Different Types Of Hackers
- What is the Foot-printing?
- Top 12 steps for Footprinting Penetration Testing
- Different types of tools with Email Footprinting
- What is “Anonymizer” & Types of Anonymizers
- Top DNS Interrogation Tools
- What is SNMP Enumeration?
- Top vulnerability scanning tools
- Information Security of Threat
- Footprinting tools:
- What is Enumeration?
- Network Security Controls
- What is Identity and Access Management?
- OWASP high TEN web application security risks
- Password Attacks
- Defend Against Key loggers
- Defend Against Spyware
- Covering Tracks
- Covering Track on Networks
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 1
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 2
- Learn more about GPS Spyware & Apparatuses
- Introduction of USB Spyware and It’s types
- 10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About
- Concepts of Denial-of-Service Attack & Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- Most Effective Ways to Overcome Impersonation on the Social Networking Site’s Problem
- How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works
- DHCP Request/Reply Messages
- DHCP Starvation Attack
- Rogue DHCP Server Attack
- IOS Switch Commands
- Web-Server Concept
- Web-Server Attacks
- Web-Server Attack Tools
- Web-Server Security Tools
- 6 Quick Methodology For Web Server Attack
- Learn Skills From Web Server Foot Printing / Banner Grabbing
- The 10 Secrets You Will Never Know About Cyber Security And Its Important?
- Ways To Learn Finding Default Content Of Web Server Effectively
- How will Social Engineering be in the Future
- Understand The Background Of Top 9 Challenges IT Leaders Will Face In 2020 Now
- Learning Good Ways To Protect Yourself From Identity Theft
- Anti-phishing Tools Guide
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



