Security administrator John Smith has noticed abnormal amounts of traffic coming from local computers at night. Upon reviewing, he finds that user data have been exfiltered by an attacker. AV tools are unable to find any malicious software, and the IDS/IPS has not reported on any non – whitelisting programs. What type of malware did the attacker use to bypass the company ‘s application whitelisting?
Option 1 : Phishing malware
Option 2 : File-less malware
Option 3 : Logic bomb malware
Option 4 : Zero-day malware
1. Phishing malware
Phishing could be a variety of social engineering attack sometimes wont to steal user data, yet as login credentials and credit card numbers. It happens once an attacker, masquerading as a trusty entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message. The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, which can lead to the installation of malware, the freezing of the system as a part of a ransomware attack or the revealing of sensitive information.
An attack can have devastating results. for individuals, this includes unauthorized purchases, the stealing of funds, or establish thieving.
Moreover, phishing is usually used to gain a foothold in company or governmental networks as a part of a bigger attack, like an advanced persistent threat (APT) event. throughout this latter scenario, employees are compromised therefore on bypass security perimeters, distribute malware within a closed setting, or gain privileged access to secured data.
An organization succumbing to such an attack typically sustains severe money losses additionally to declining market share, reputation, and consumer trust. depending on scope, a phishing try would possibly intensify into a security incident from that a business will have a difficult time recovering.
2. File-less malware
Fileless malware could be a type of malicious software that uses legitimate programs to infect a pc. It doesn’t rely on files and leaves no footprint, making it difficult to and remove and take away. modern adversaries understand the ways organizations use to try to dam their attacks, and they’re crafting more and more refined, targeted malware to evade defenses. It’s a race against time, as the most effective hacking techniques ar sometimes the newest ones. Fileless malware has been effective in evading all but the most sophisticated security solutions.
Fileless malware emerged in 2017 as a thought style of attack, however several of those attack methods are around for a moment. Frodo, range of the Beast, and therefore the Dark attacker were all early samples of this kind of malware. newer, high-profile fileless attacks include the hack of the Democratic National Committee and therefore the Equifax breach.
What makes fileless infections thus insidious is additionally what makes them thus effective. There are claims that fileless malware is “undetectable.” This isn’t virtually true, it simply means that fileless attacks are typically undetectable by antivirus, whitelisting, and other traditional end security solutions. In fact, the Ponemon Institute claims that fileless attacks are ten times more doubtless to succeed than file-based attacks.
How will a fileless attack happen?
The application whitelisting in this fileless attacks constitute the broader class of low-observable characteristics (LOC) attacks, a kind of stealth attack that evades detection by most security solutions and frustrates forensic analysis efforts. whereas not thought-about a traditional virus, fileless malware will add a similar way—it operates in memory. without being hold on in a file or put in directly on a machine, fileless infections go straight into memory and the malicious content never touches the disk drive. several LOC attacks take advantage of Microsoft Windows PowerShell, a legitimate and useful tool employed by administrators for task automation and configuration management. PowerShell consists of a command-line shell and associated scripting language, providing adversaries with access to simply about everything and something in Windows.
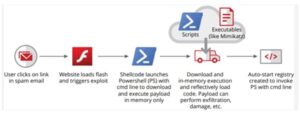
The figure above illustrates however a fileless attack will happen. Like most advanced attacks today, fileless attacks typically use social engineering to induce users to click on a link or an attachment during a phishing email. Fileless attacks are usually used for lateral movement, that means they create their method from one device to the next with the objective of gaining access rights to valuable data across the enterprise network. To avoid suspicion, fileless malware gets into the inner recesses of sure, whitelisting applications (like PowerShell and Windows script host executables like wscript.exe and cscript.exe) or the operating system to initiate malicious processes. These attacks abuse the trust model used by security whitelisting applications to not monitor whitelisting programs.
What is vital to notice within the on top of scenario is that the hacker failed to ought to figure out the way to sneak a malicious program past antivirus and malware defense. Most automated sensors cannot notice statement alterations. A trained analyst will determine these scripts, however typically doesn’t understand wherever to seem within the first place of whitelisting applications.
3. Logic bomb malware
A logic bomb may be a piece of code intentionally inserted into a software system that will set off a malicious function when such conditions are met. as an example, a programmer may hide a chunk of code that starts deleting files (such as a remuneration info trigger), ought to they ever be terminated from salary.
Software salary inherently malicious, like viruses and worms, usually contain logic bombs that execute a certain payload at a pre-defined time or once another condition is met. this system may be employed by a virus or worm to realize momentum and unfold before being detected. Some viruses attack their host systems on specific dates, like friday the thirteenth or april fools’ Day. Trojans and alternative laptop viruses that activate on bound dates are usually known as “time bombs”.
To be considered a logic bomb, the payload ought to be unwanted and unknown to the user of the software. As an example, trial programs with code that disables bound functionality when a group time aren’t normally regarded as logic bombs.
4. Zero-day malware
A zero-day (also called 0-day) vulnerability may be a computer-software vulnerability that’s unknown to those who should have an interest in mitigating the vulnerability (including the vendor of the target software). till the vulnerability is mitigated, hackers will exploit it to adversely an pc programs, data, extra computers or a network. An exploit directed at a zero-day is named a zero-day exploit, or zero-day attack.
The term “zero-day” originally mentioned the number of days since a brand new piece of software was discharged to the public, thus “zero-day” software was software that had been obtained by hacking into a developer’s computer before release. Eventually the term was applied to the vulnerabilities that allowed this hacking, and to the number of days that the vendor has had to mend them. Once the seller learns of the vulnerability, they will sometimes create patches or advise workarounds to mitigate it.
The more recently that the vendor has become aware of the vulnerability, the additional likely it’s that no fix or mitigation has been developed. Once a fix is developed, the chance of the exploit succeeding decreases as additional users apply the fix over time. For zero-day exploits, unless the vulnerability is inadvertently fixed, like by an unrelated update that happens to mend the vulnerability, the likelihood that a user has applied a vendor-supplied patch that fixes the matter is zero, therefore the exploit would stay available. Zero-day attacks are a severe threat.
Learn CEH & Think like hacker
- What is Ethical Hacking? & Types of Hacking
- 5 Phases of Hacking
- 8 Most Common Types of Hacker Motivations
- What are different types of attacks on a system
- Scope and Limitations of Ethical Hacking
- TEN Different Types Of Hackers
- What is the Foot-printing?
- Top 12 steps for Footprinting Penetration Testing
- Different types of tools with Email Footprinting
- What is “Anonymizer” & Types of Anonymizers
- Top DNS Interrogation Tools
- What is SNMP Enumeration?
- Top vulnerability scanning tools
- Information Security of Threat
- Footprinting tools:
- What is Enumeration?
- Network Security Controls
- What is Identity and Access Management?
- OWASP high TEN web application security risks
- Password Attacks
- Defend Against Key loggers
- Defend Against Spyware
- Covering Tracks
- Covering Track on Networks
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 1
- Everything You Need To Know About Sniffing – Part 2
- Learn more about GPS Spyware & Apparatuses
- Introduction of USB Spyware and It’s types
- 10 Types of Identity Theft You Should Know About
- Concepts of Denial-of-Service Attack & Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- Most Effective Ways to Overcome Impersonation on the Social Networking Site’s Problem
- How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works
- DHCP Request/Reply Messages
- DHCP Starvation Attack
- Rogue DHCP Server Attack
- IOS Switch Commands
- Web-Server Concept
- Web-Server Attacks
- Web-Server Attack Tools
- Web-Server Security Tools
- 6 Quick Methodology For Web Server Attack
- Learn Skills From Web Server Foot Printing / Banner Grabbing
- The 10 Secrets You Will Never Know About Cyber Security And Its Important?
- Ways To Learn Finding Default Content Of Web Server Effectively
- How will Social Engineering be in the Future
- Understand The Background Of Top 9 Challenges IT Leaders Will Face In 2020 Now
- Learning Good Ways To Protect Yourself From Identity Theft
- Anti-phishing Tools Guide
This Blog Article is posted by
Infosavvy, 2nd Floor, Sai Niketan, Chandavalkar Road Opp. Gora Gandhi Hotel, Above Jumbo King, beside Speakwell Institute, Borivali West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400092
Contact us – www.info-savvy.com



